How Long Does 3D Printing Take? Unveiling the Time Factors
3D printing can take anywhere from a few minutes to several days. The duration depends on the object's size, complexity, and material used.
3D printing is a revolutionary technology transforming manufacturing and prototyping. It allows for the creation of complex structures with precision and efficiency. Smaller objects with simple designs typically take a few minutes to a few hours to print. Larger, more intricate items can require several days to complete.
Factors such as print resolution, layer height, and material type significantly influence the time required. Rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing are made possible through 3D printing, offering unparalleled flexibility. This technology continues to evolve, promising faster print times and broader applications in various industries.
Introduction To 3d Printing
3D printing has revolutionized the way we create objects. It allows us to make complex shapes and designs with ease. This technology is both fascinating and accessible. Understanding its basics can help anyone appreciate its impact.
Brief History
3D printing started in the 1980s. The first 3D printer was invented by Chuck Hull in 1984. It was called stereolithography. This technology used UV light to harden liquid plastic into shapes. Over the years, 3D printing evolved rapidly. New methods and materials were developed. Today, it is an essential tool in many industries.
Modern Applications
3D printing is used in various fields. It is popular in medicine, where it helps create custom prosthetics and implants. In the automotive industry, it is used to prototype parts quickly. It also plays a significant role in education, allowing students to visualize and create models. Artists and designers use 3D printing to bring their ideas to life.
Here are some common uses:
- Prototyping new products
- Creating medical implants
- Manufacturing custom tools
- Making art and sculptures
The versatility of 3D printing is astounding. It continues to open new possibilities.
Key Time Factors
Understanding the time required for 3D printing depends on various key factors. These factors influence the overall duration of the printing process. Let's delve into the primary elements that impact 3D printing times.
Printer Type
The type of 3D printer you use significantly affects the printing speed. Different printers have varying capabilities and limitations. Here are some common printer types:
- FDM Printers: These printers are generally slower but more affordable.
- SLA Printers: They offer higher detail but take longer to print.
- SLS Printers: These are faster but more expensive and complex.
Material Choice
The material you choose for printing also impacts the duration. Different materials have unique properties and print times. Consider these common materials:
| Material | Print Speed |
|---|---|
| PLA | Fast |
| ABS | Moderate |
| Resin | Slow |
Choosing the right material can help optimize your 3D printing time.
Impact Of Design Complexity
The time it takes to complete a 3D print largely depends on the complexity of the design. Simple designs and intricate models can vary greatly in printing duration. Understanding these differences can help manage expectations and plan projects more effectively.
Simple Designs
Simple designs are basic shapes and structures. They usually have fewer details and smoother surfaces. These designs are quick to print. They often take a few minutes to a few hours.
- Basic geometric shapes like cubes and spheres
- Low-detail prototypes
- Functional parts with minimal detail
For example, a small cube might take less than an hour to print. A basic smartphone stand could take around 2-3 hours. The simplicity of the design reduces the print time significantly.
Intricate Models
Intricate models involve detailed features and complex structures. These designs require more time to print. They can take several hours to several days.
- Highly detailed figurines
- Complex mechanical parts
- Artistic sculptures with fine details
For example, a detailed miniature of a building might take 10-15 hours to print. An intricate art sculpture could take 24-48 hours. The more complex the model, the longer the print time.
Here's a table to summarize the impact of design complexity on 3D printing time:
| Design Type | Estimated Print Time |
|---|---|
| Simple Designs | Minutes to a few hours |
| Intricate Models | Several hours to days |

Credit: prtwd.com
Role Of Printer Settings
Understanding the role of printer settings is crucial in determining how long a 3D print will take. Different settings can significantly alter print times, affecting both the quality and speed of the final product. Let's dive into two critical settings: Layer Height and Print Speed.
Layer Height
The layer height refers to the thickness of each printed layer. A smaller layer height results in higher resolution but takes more time. Conversely, a larger layer height speeds up the print but may reduce detail.
Here's a quick comparison:
| Layer Height (mm) | Print Quality | Print Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | High | Slow |
| 0.2 | Medium | Moderate |
| 0.3 | Low | Fast |
For detailed models, use a smaller layer height. For quick prototypes, a larger layer height suffices.
Print Speed
Print speed directly affects the duration of your 3D print. Faster speeds can save time but may compromise quality. Slower speeds enhance detail but take longer.
Consider these speed settings:
- Slow Speed (30-50 mm/s): Best for detailed prints.
- Medium Speed (60-80 mm/s): Balanced quality and speed.
- High Speed (100+ mm/s): Ideal for quick drafts.
Adjusting print speed helps balance time and quality. Always test different speeds for optimal results.
Post-processing Time
After the printer finishes, the work is not done. The post-processing time can vary. This involves steps to make the print look great and function well. Below are two key steps in post-processing: cleaning and finishing, and assembly.
Cleaning And Finishing
The first step is cleaning the print. Removing support structures is crucial. Use pliers or a knife to cut these away. Next, wash the print to remove any leftover resin or powder. For FDM prints, sandpaper can smooth rough edges. Start with coarse grit and move to fine grit.
Finishing may involve painting or sealing. Primer helps paint stick well. After priming, add the final paint. Seal the print with a clear coat for protection. This can take several hours or even days, depending on the complexity.
Assembly
Some 3D prints come in multiple parts. Assembling these parts is another step. Use glue or screws to connect parts. Ensure all pieces fit correctly. This may involve more sanding or trimming.
Assembly can be time-consuming. Complex models can take hours to put together. Simple models may only need a few minutes.
| Step | Time Required |
|---|---|
| Removing Supports | 5-30 minutes |
| Sanding | 30-60 minutes |
| Priming and Painting | 1-3 days |
| Assembly | 10 minutes to several hours |
Each of these steps adds to the total time. Planning ahead can help manage this time effectively. Keep these steps in mind for accurate project timelines.
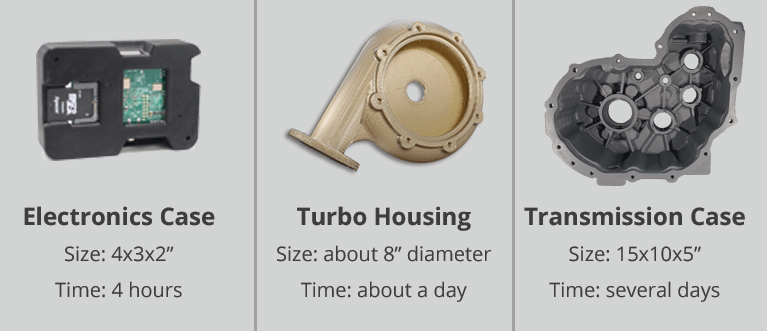
Credit: 3space.com
Comparison Of Different Technologies
Understanding how long 3D printing takes requires examining different technologies. Various methods come with unique time frames and processes. This section compares FDM, SLA, SLS, and DMLS.
Fdm Vs. Sla
| Feature | FDM | SLA |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Time | Several hours to days | Several hours |
| Material | Plastic filaments | Liquid resin |
| Quality | Good for prototypes | High resolution |
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) uses plastic filaments. The print speed can vary based on size and complexity. Small parts may take a few hours. Large or detailed parts can take days.
Stereolithography (SLA) uses liquid resin cured by a laser. It generally offers faster print times than FDM. SLA is ideal for high-resolution prints. Small parts are often completed within hours.
Sls Vs. Dmls
| Feature | SLS | DMLS |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Time | Several hours to days | Several hours to days |
| Material | Nylon, glass-filled nylon | Metal powders |
| Quality | Durable parts | High-strength metal parts |
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses a laser to fuse powder materials. It is suitable for strong, durable parts. Print times can vary. Small parts may finish in hours. Larger parts may take days.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) works similarly to SLS but uses metal powders. This method is ideal for high-strength metal parts. Printing times are similar to SLS. Small parts may take hours, while large parts may take days.
Real-world Examples
Understanding how long 3D printing takes can be easier with real-world examples. Here, we explore two case studies: rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing. These examples highlight the time involved in each process and the benefits they bring.
Case Study: Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is essential for product development. It allows designers to create models quickly. Below is a table summarizing the time taken for different objects:
| Object | Print Time |
|---|---|
| Simple Keychain | 1-2 hours |
| Phone Case | 3-4 hours |
| Detailed Miniature | 6-8 hours |
For example, a simple keychain may take just 1-2 hours. A phone case might require 3-4 hours. For a detailed miniature, expect 6-8 hours. Rapid prototyping helps to test designs quickly.
Case Study: Custom Manufacturing
Custom manufacturing often involves more complex designs. The time varies based on the object's size and detail. Here's a list of custom items and their print times:
- Customized Jewelry: 2-5 hours
- Car Parts: 10-12 hours
- Medical Implants: 20-24 hours
Customized jewelry takes around 2-5 hours. Car parts can take 10-12 hours. Medical implants might need 20-24 hours. Custom manufacturing ensures each piece is unique and precise.
Tips For Reducing Print Time
3D printing can take a long time. But there are ways to make it faster. Here are some tips to reduce print time and get your projects done quickly.
Optimizing Designs
Designs with many details take longer to print. Simplify your design to cut down on print time. Use fewer intricate details and keep shapes simple.
Hollow out solid designs to save time. A hollow model uses less material and prints faster.
- Reduce the number of supports needed.
- Avoid overhangs and steep angles.
- Use fewer layers for faster prints.
Choosing The Right Printer
Not all 3D printers are the same. Some are faster than others. Choose a printer that matches your speed needs.
| Printer Type | Speed |
|---|---|
| FDM | Moderate |
| SLA | Fast |
| DLP | Very Fast |
Use a printer with a larger nozzle for faster prints. Smaller nozzles take longer to print the same model.
Follow these tips to reduce 3D printing time. This will help you complete projects faster and more efficiently.
Future Trends
The world of 3D printing is evolving rapidly. Future trends promise faster and more efficient printing. This section explores two key areas shaping the future of 3D printing: Advancements in Speed and Innovations in Materials.
Advancements In Speed
Speed is a critical factor in 3D printing. New technologies are emerging to reduce printing time. Faster printers are being developed to meet growing demand. These printers use advanced techniques like parallel processing and multi-nozzle systems. Parallel processing can print multiple parts at once. Multi-nozzle systems can print different materials simultaneously.
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) is another breakthrough. CLIP uses light and oxygen to print objects quickly. This method can produce parts in minutes instead of hours. Table below shows a comparison of traditional vs CLIP printing speeds:
| Method | Average Print Time |
|---|---|
| Traditional 3D Printing | 5-10 hours |
| CLIP | 5-10 minutes |
Innovations In Materials
Material innovation is pushing the limits of 3D printing. New materials are being developed for stronger and more durable prints. Composite materials combine different elements to enhance properties. For example, carbon fiber-infused filaments offer high strength and lightweight properties.
Biodegradable materials are also becoming popular. These materials are eco-friendly and reduce waste. Recycled materials can be used to print new objects, promoting sustainability. List of popular materials:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid)
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
- Carbon Fiber Composites
- Metal Filaments
Smart materials are another exciting trend. These materials change properties in response to stimuli. For instance, shape-memory polymers return to their original shape when heated. This opens up new possibilities for innovative designs.
Credit: www.quora.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Does It Take So Long To 3d Print?
3D printing takes time due to layer-by-layer construction. Precision and complexity of the design also affect speed. High-quality prints require slow, careful movements.
How Long Does It Take To 3d Print At Home?
3D printing at home typically takes 1 to 12 hours, depending on the object's size and complexity.
How Fast Can You 3d Print?
The speed of 3D printing varies by machine and material. Typically, it ranges from 40mm to 150mm per second.
Is It Normal For 3d Prints To Take Days?
Yes, it's normal for 3D prints to take days. Large or highly detailed prints often require extended time.
Conclusion
Understanding the time required for 3D printing helps in planning projects efficiently. Factors like material and complexity impact duration. By considering these aspects, you can better manage your expectations. Stay informed and make the most of your 3D printing endeavors.
Happy printing!

